Survival function
To estimate the surviving fraction (SF) of specific cells, the two-lesion kinetics (TLK) model proposed by Stewart et al. [1] can be used. The TLK model includes kinetic processes of fast- and slow-DNA repair, and, based on lethal DNA damage, it can calculate the SF of a cell population. It must be stated that multiple-lesion repair mechanisms may lead to complex aberrations due to incorrect rejoining.
The SF is calculated based on the function:
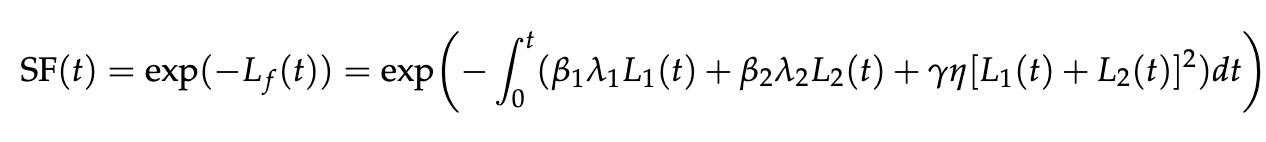
- L1(t) is the number of lesions per cell in the fast-repair process at a given time t after the beginning of the irradiation procedure.
- L2(t) is the number of lesions per cell in the slow-repair process at a given time t.
- Lf(t) is the number of lethal lesions that may lead to cell death at time t.
This model includes:
- Repair probability coefficients, which represent the rate of rejoined lesions (λ and η), and
- Lethality probability coefficients, which represent the probability that a residual lesion may lead to cell death (β and γ). More specifically, λ1, λ2, and η correspond to fast-, slow-, and binary-rejoining processes, respectively (expressed in /hour). Similarly, β1, β2, and γ correspond accordingly to each rejoining process.
The two-lesion kinetics (TLK) [1] model includes kinetic processes of fast- and slow-DNA repair, and, based on lethal DNA damage, it can calculate the SF of a cell population
User guide
To run the code, users need to open a terminal in the folder repair_survival_models containing the molecularDNAsurvival.py script.
Then,
python3 molecularDNAsurvival.py
Input parameters
At line 13, users need to set the name of the output file, which is print in text format.
outputFile = "molecularDNAsurvival.txt"
At line 14, users need to set the name of the input file, which for the current version is in root format. A future update of moleculardna will include the option for using SDD files.
iRootFile = "../molecular-dna.root"
At line 18, users need to define the dimensions of the cell (x, y, z) in meters.
r3 = 7100*1e-09 * 2500*1e-09 * 7100*1e-09
At line 19, users need to define the length (in bp) of the DNA molecule model included in the simulation. The length of the DNA included in the “human cell” example is 6405886128 bp.
NBP = 6405886128
At line 20, the code calculates the mass of the cell used in the simulation. If another cell shape has been defined, other than the ellipsoid, the user needs to modify this calculation.
mass = 997 * 4 * 3.141592 * r3 / 3
Model parameters
The TLK model, calculates the survival fraction of cells for specific time points, with the integral values being 1 Gy. Users need to define the maximum dose, for which the calculation will end.
maxDose = 9
This is the dose rate used in the TLK model to calculate survival:
DR1 = 60 #Gy/h SF-dose
This is a constant of the model, as defined by Stewart in the TLK [1]. It defines the length of DNA included in the cell:
NBP_of_cell = 4682000000
Normalization factor to define the true size of the cell used in the simulation:
bp = NBP_of_cell/NBP
For the definition of the parameter values λ1, λ2, β1, β2, γ, η, the following values correspond to the output implemented in [2].
gamma = 0.189328
Lamb1 = 0.0125959
Lamb2 = 1
Beta1 = 0.0193207
Beta2 = 0
Eta = 7.50595e-06
Definition of the name of the cells: it is just a name for the output.
cell = "test"
References
[1] Two-lesion kinetic model of double-strand break rejoining and cell killing, R. D. Stewart, Radiat. Res. 156 (2001) 365-378 - link
[2] Simulation of DNA damage using Geant4-DNA: an overview of the “molecularDNA” example application, K. Chatzipapas et al. Prec. Radiat. Oncol. 7 (2023) 4-14 - link