Parameter study (cylinders.mac)
Table of contents
Overview
The simulation geometry is based upon a past parameter study [1] of direct and indirect DNA damage yields in straight DNA fibres to study the impacts of the different parameters. The cylinders.mac macro file can be used for such simulation.
Geometry
The geometry for parameter sweeps consists of a 3 μm sphere filled with 200.000 individual 216 bp long straight DNA segments in a 100 nm × 30 nm × 30 nm placement volume. Radical kill distance Damage model is set to 9 nm and the range for direct interaction is set to 6 A.
# Geometry: size of World volume
/world/worldSize 10200 nm
# Geometry: size of cell volume
/cell/radiusSize 3 3 3 um
# Chemistry: end time of chemistry stage
/scheduler/endTime 1 us
# Geometry: optimisation of voxelisation
/dnageom/setSmartVoxels 1
# Geometry: check overlaps in DNA geometry region
/dnageom/checkOverlaps false
# Geometry: distance from base pairs at which radicals are killed
/dnageom/radicalKillDistance 9 nm
# Geometry: deposited energy accumulation range limit to start recording SBs from direct effects
/dnageom/interactionDirectRange 6 angstrom
# Geometry: creation
# - Side length for each placement
/dnageom/placementSize 30 30 100 nm
# - Scaling of XYZ in fractal definition file
/dnageom/fractalScaling 1 1 1 nm
# - Path to file that defines placement locations
/dnageom/definitionFile geometries/prisms200k_r3000.txt
# - Set a placement volume
/dnageom/placementVolume prism geometries/straight-216-0.txt
# Geometry: take the angles in the voxel placement file as multiples of pi
/dnageom/setVoxelPlacementAnglesAsMultiplesOfPi false
# Geometry: enable custom molecule sizes
/dnageom/useCustomMoleculeSizes false
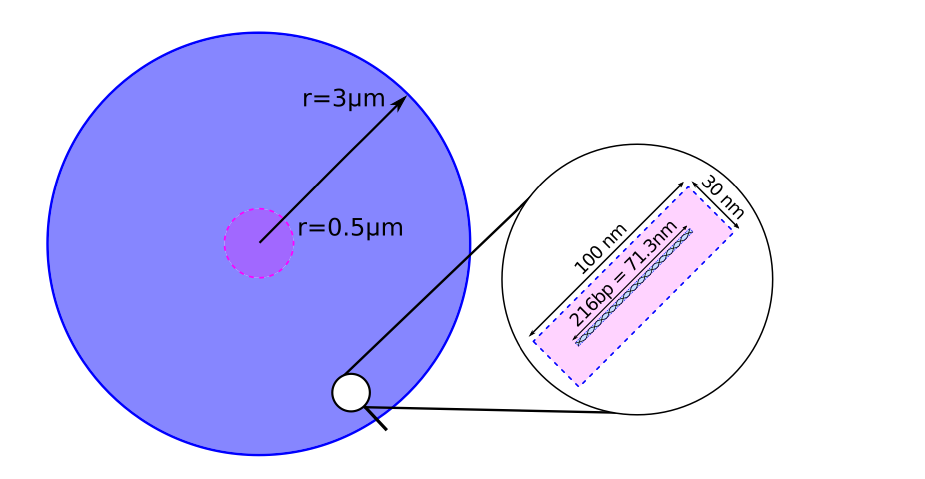
A spherical chromosome named “cylinder” is defined for analysis using:
/chromosome/add cylinder sphere 3000 0 0 0 nm
Particle source
Primary electrons are generated randomly, with a random direction in a smaller 500 nm sphere in the centre of the test region. The primary particles with energies no greater than 4.5 keV cannot escape the larger spherical region, and all primaries see an equivalently random region.
# Source geometry
/gps/pos/type Volume
/gps/pos/shape Sphere
/gps/pos/radius 500 nm
/gps/pos/centre 0 0 0 nm
# Source particle, energy and angular distribution
/gps/particle e-
/gps/energy 4.5 keV
/gps/ang/type iso
# Beam on
/run/beamOn 100000
Damage model
Direct damage model uses the 17.5 eV for lower and upper break thresholds.
/dnadamage/directDamageLower 17.5 eV
/dnadamage/directDamageUpper 17.5 eV
/dnadamage/indirectOHBaseChance 1.0
/dnadamage/indirectOHStrandChance 0.65
/dnadamage/inductionOHChance 0.0
/dnadamage/indirectHBaseChance 1.0
/dnadamage/indirectHStrandChance 0.65
/dnadamage/inductionHChance 0.0
/dnadamage/indirectEaqBaseChance 1.0
/dnadamage/indirectEaqStrandChance 0.65
/dnadamage/inductionEaqChance 0.0
Results
Output (see analysis) is analysed by using the cylinders.C ROOT macro file.
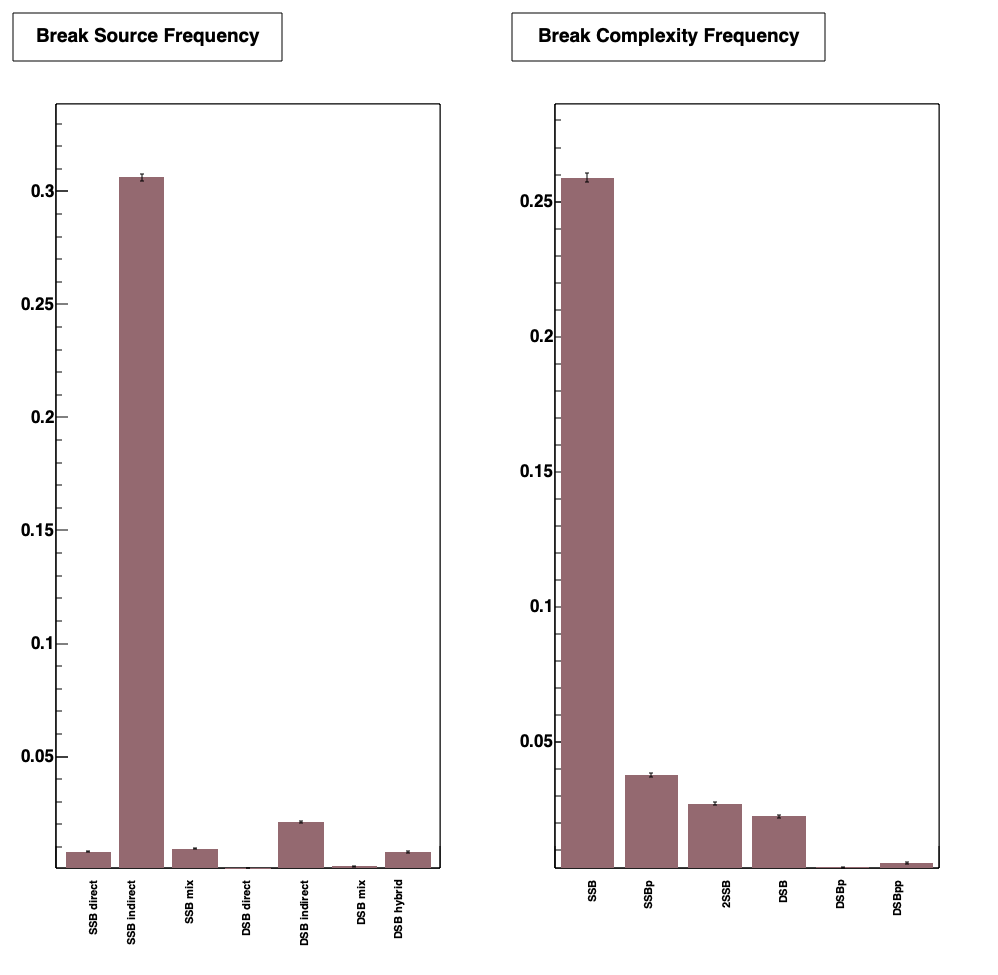
Refer classification model for detail of source and complexity frequency.
Visualization
For visualization, we recommend to use the simple DNA fiber geometry provided in fiber.mac. More specifically, start moleculardna using the command:
./molecular –t 1 –v 1
to open the Qt visualiser. Then use the mac file that you want, e.g.
/control/execute fiber.mac
You can then use the graphical interface Reset Camera button to get visualization.
References
[1] Computational modelling of lowenergy electron-induced DNA damage by early physical and chemical events, H. Nikjoo et al., Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 71 (1997) 467–483 - link